
Electricity
All you need to know!


Electrical diagram
![]() Electricity
Electricity
Essential elements to know
Electrical voltage
Electrical power
Direct current
Alternating current
Electrical energy
Electrical circuits
Electronic components
![]() Printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
What is a printed circuit board (PCB)?
A printed circuit board (PCB) is an insulating substrate usually made of a composite material, such as FR4, on which electronic components are mounted to form functional electronic circuits.
With ICAPE GROUP, PCBs are used in a multitude of electronic applications, from consumer devices such as cell phones and computers to industrial and medical equipment. Their design and manufacture have evolved to meet the growing demands of :
Miniaturization
Performance
Reliability of electronic devices
Types of network
Power supply systems
Each type of power network is designed to meet specific needs in terms of electricity distribution and consumption, according to different geographical areas and varying consumer demands.

Power grids
Designed to transport large quantities of electricity
They use transmission lines to carry electricity generated by power plants to substations located closer to consumption areas.

Power stations
Plants designed to generate electricity on a large scale
The choice of power plant often depends on available resources, geographical location and environmental considerations.

Power distribution
Medium-voltage (MV) and low-voltage (LV) distribution networks
Medium-voltage distribution networks carry electricity to more specific areas, such as residential neighborhoods, industrial or commercial zones.
How does your home's electrical installation work?
Electrical installation
![]() Installation to standards
Installation to standards
Principle of a domestic electrical installation
The basic principle of a domestic electrical installation is to secure the distribution of electricity to meet the needs of the home, while complying with safety standards.
All domestic electrical installations must comply with local and national electrical standards. These standards govern the design, installation and maintenance of electrical systems to ensure the safety of occupants.
Earth leakage circuit breaker
A fundamental element in an electrical circuit to ensure the safety of people and equipment.
Earthing system
Its operation relies on diverting unwanted currents to the ground to avoid the risk of electrocution and fire.
Distribution board
Groups together various electrical protection and distribution devices in a cabinet or box.
Wires and circuits
Key elements of an electrical installation, facilitating the safe distribution of electricity throughout a home.
Mandatory electrical diagnosis
Mandatory electrical diagnostics involve assessing the safety of a home’s electrical installation as part of a property sale.
The importance of the electricity meter
It is a central device in an electrical installation, measuring electricity consumption, enabling precise monitoring of consumption, detection of potential problems and helping to maintain the stability of the electrical network.
Technology development
![]() Electrical innovations
Electrical innovations
A section to keep abreast of trends
Cutting-edge technologies to improve the distribution and management of electricity.
They use modern technologies such as sensors, communication systems and data management software to collect real-time information on electricity consumption and production.
Sensor technology in electronics
Detecting and measuring various physical or chemical phenomena.
There is a wide variety of sensors, each designed to meet specific needs. For example, temperature sensors use variations in resistance, etc.
Storage solutions
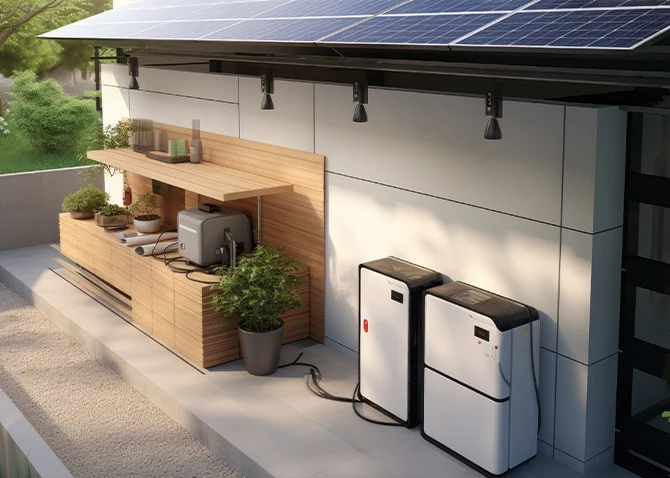
![]() Energy storage
Energy storage
Batteries for everyone!
Advances in energy storage technologies have given rise to a variety of solutions, including batteries for different uses.
Lithium-polymer (Li-pol) batteries, for example, are similar to Li-ion batteries in that they offer greater flexibility and can be adapted to different shapes, making them ideal for compact electronic devices.

